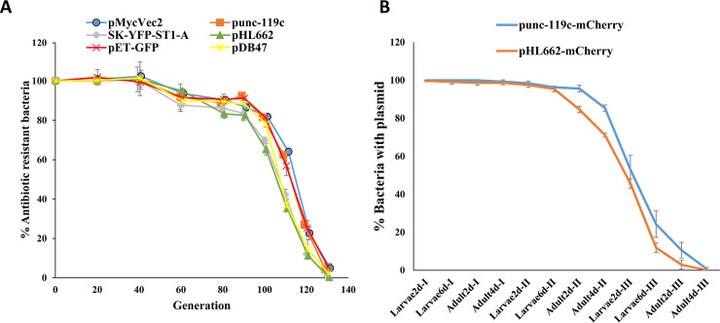
Abstract
Presently, the principal tools to combat malaria are restricted to killing the parasite in infected people and killing the mosquito vector to thwart transmission. While successful, these approaches are losing effectiveness in view of parasite resistance to drugs and mosquito resistance to insecticides. Clearly, new approaches to fight this deadly disease need to be developed. Recently, one such approach–engineering mosquito resident bacteria to secrete anti-parasite compounds–has proven in the laboratory to be highly effective. However, implementation of this strategy requires approval from regulators as it involves introduction of recombinant bacteria into the field. A frequent argument by regulators is that if something unexpectedly goes wrong after release, there must be a recall mechanism. This report addresses this concern. Previously we have shown that a Serratia bacterium isolated from a mosquito ovary is able to spread through mosquito populations and is amenable to be engineered to secrete anti-plasmodial compounds. We have introduced a plasmid into this bacterium that carries a fluorescent protein gene and show that when cultured in the laboratory, the plasmid is completely lost in about 130 bacterial generations. Importantly, when these bacteria were introduced into mosquitoes, the bacteria were transmitted from one generation to the next, but the plasmid was lost after three mosquito generations, rendering the bacteria non-recombinant (wild type). Furthermore, no evidence was obtained for horizontal transfer of the plasmid to other bacteria either in culture or in the mosquito. Prior to release, it is imperative to demonstrate that the genes that thwart parasite development in the mosquito are safe to the environment. This report describes a methodology to safely achieve this goal, utilizing transient expression from a plasmid that is gradually lost, returning the bacterium to wild type status.